Whether it’s moving batch transactions to an outsourced payroll provider or delivering a digital video for a marketing campaign, file transfer is at the heart of many business processes. As a result, there’s a greater need to move data quickly and securely. This has also created new workload requirements, with higher-frequency batches and larger files.
There are several ways to transfer files from one computer to another. Using software like FTP or SFTP allows for the secure upload and download of files from an online server. A more simple way to transfer files is by using a USB or Ethernet cable to connect two computers side-by-side. These types of connections can be used in addition to other methods of file transfer, including using a null modem cable or parallel port.
When transferring large files, the file size and transfer speed are important factors in determining how long it takes to complete the transfer. However, estimating how long it will take to transfer a file can be difficult, and the actual time may vary slightly depending on the circumstances. Fortunately, there are many tools available that can help estimate the time it will take to transfer a file.
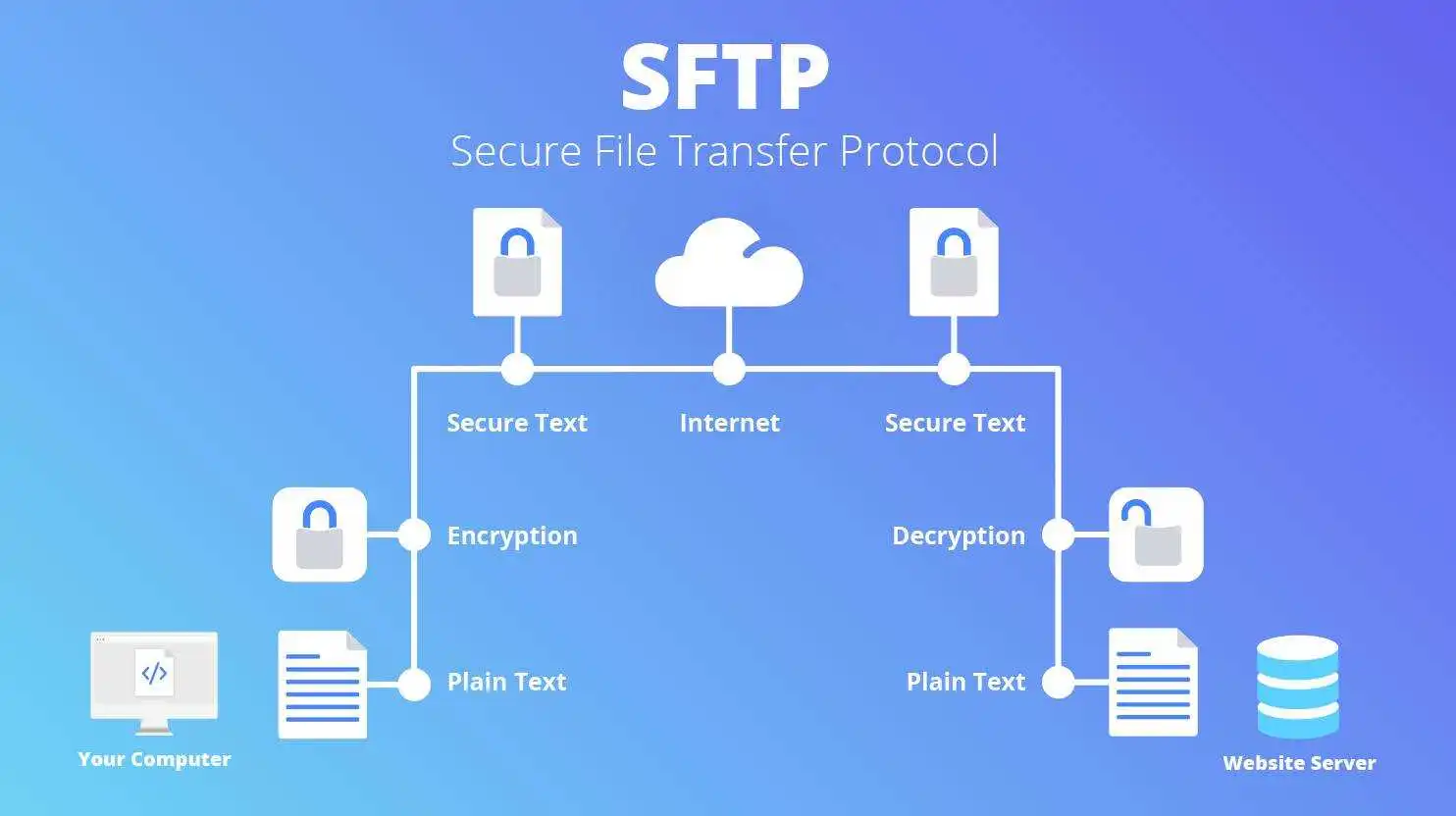
The most common method of file transfer is via email. While this is a convenient and quick method, it can be insecure and open up your organization to hackers. The Secure File Transfer System (SFTS) provides a web-based alternative to email and is the recommended method for transferring large files.
Other methods of file transfer include faxing or physically connecting the two computers with a wire. These methods are not as efficient as a managed file transfer solution, but they are useful for transferring small files that aren’t highly sensitive.
When choosing a file transfer protocol, it’s crucial to consider the needs of your organization and the intended recipients. Some use cases lend themselves more to a certain protocol than others, so it’s good to have multiple options for your customers to choose from.
Another factor in deciding what type of file transfer protocol to implement is the available hardware and network resources. For example, the speed of a hard drive will have a significant impact on the time it takes to transfer files from an external device.
A data transfer rate measures how much digital data can be transferred over a network connection. This information is typically displayed as bits per second or kilobytes per second. For example, you may see internet service providers advertise their broadband or fibre connection speed as Mbps or KBps. A bit is the smallest unit of data, and there are eight bits in every byte. The higher the data transfer rate, the faster the transmission speed. Similarly, the more storage space on an external device, the faster it can transfer files. This is why it’s important to keep your data storage and transfer rates up-to-date.Send Big Files